NFC antenna

NFC antenna
Features
-
01
Small and low-profile design
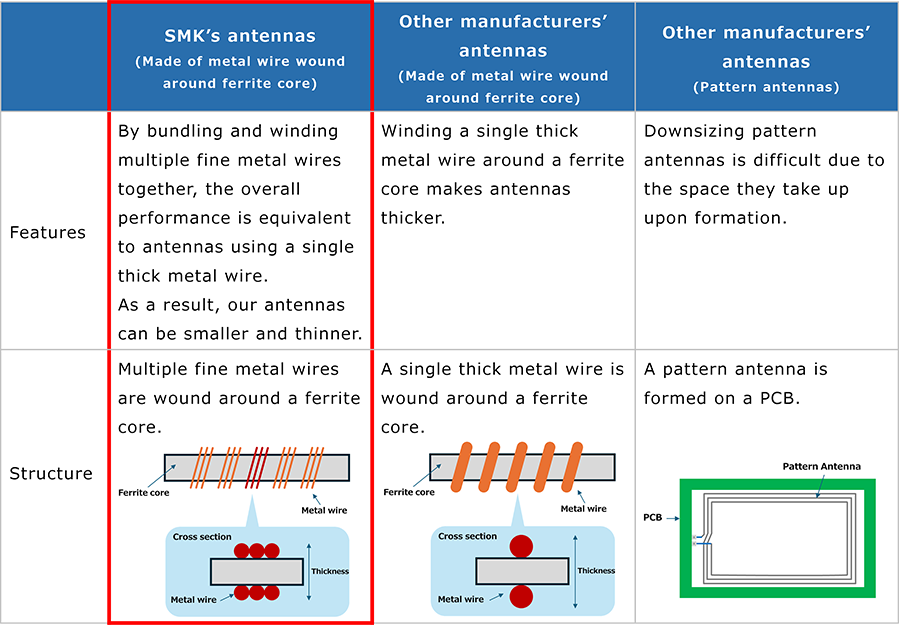
A coil antenna that is made of fine metal wires wound around a ferrite core.* Our original winding structure achieves a small and low-profile design.
-
02
Can be set up near metal
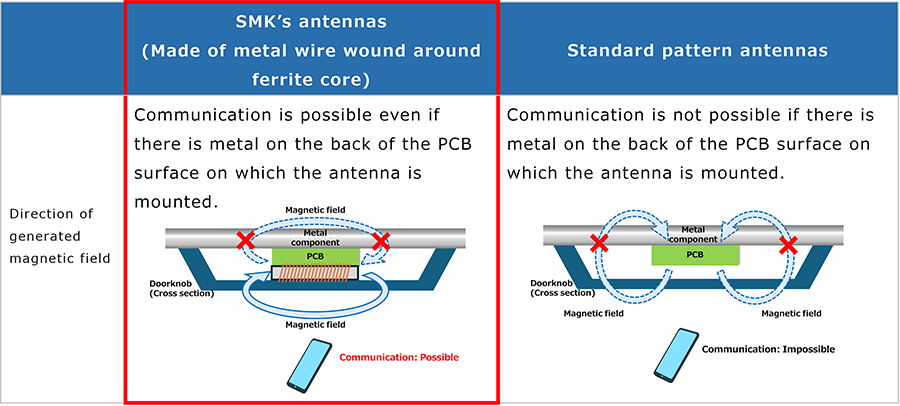
Communication is possible even if there are metal cases or components on the back of the PCB surface on which the antenna is set up. It is also possible to set the antenna up near metal.
-
03
Designed for reflow soldering
Our antenna is designed for reflow soldering, which improves process efficiency.
*Patent numbers: No.6292240、 No.6468376、 No.6424913 (Click on the left to visit the INPIT's "About Japan Platform for Patent Information" page.)
●NFC antenna comparison chart
●The basis of immunity towards metal influence
Use cases
Our antennas can be used in a wide variety of applications, owing to their features such as small size, low-profile design, and immunity to surrounding metal.
-
Smart watches
The antenna embedded in a metal frame enables cashless payment.
-

-
Smart locks
The antenna built into a doorknob allows smartphones or cards to be used as keys.
-

-
Wearable devices
The antenna built into a compact wearable device, such as wireless earbuds, enables connection to the device you want to pair easily.
-

-
Displays
Touch operation of a display is enabled by installing the antenna near or on the back of the display. This is difficult with pattern antennas.
-

-
Car doorknobs/pillars
The antenna built into a car doorknob or pillar allows smartphones or cards to be used as car keys.
-

-
Motorcycle gauges
The antenna built into a motorcycle gauge allows smartphones or cards to be used as motorcycle keys.
-

Product Specifications
The antenna’s structure consists of multiple fine metal wires wound around a ferrite core.
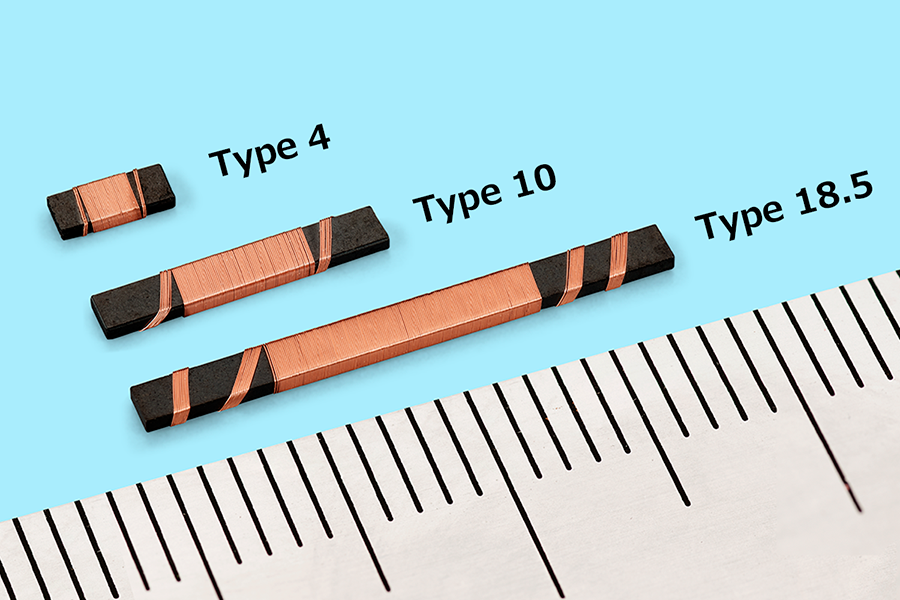
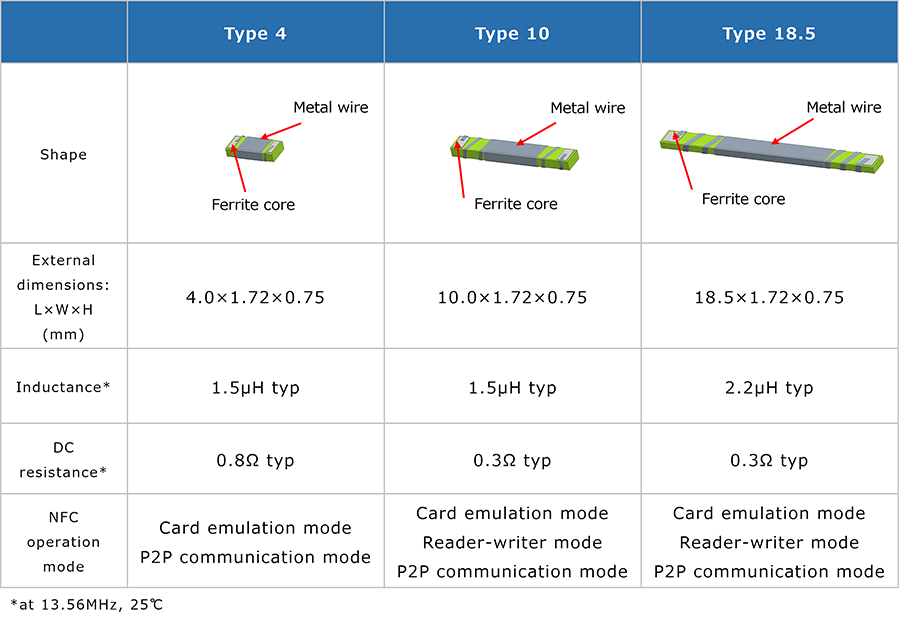
Three modes of operation
| Reader/Writer Mode | Mode that allows smartphones to be used as reading devices [Application examples] - Poster advertisements (the same use as QR codes)/Sending or extracting settings or logs from data collection devices for thermometers or pedometers/Rewriting electronic price tags - Pairing with Bluetooth devices |
| Card Emulation Mode | Mode that allows smartphones to be used as tags and embedded devices to be used as readers [Application examples] - Security locks (combined use of card and smartphone) - Electronic payments in stores/Membership or loyalty cards for fitness or other clubs |
| Peer-to-Peer Mode | Mode that allows smartphones to operate at the same level as embedded devices [Application examples] - Data exchange between smartphones - Data exchange between smartphone and PC - Sending Wi-Fi settings to embedded devices |
■What does NFC mean?
NFC is an abbreviation for “Near Field Communication”. NFC is an international standard for near field communication technology that uses the 13.56 MHz frequency band. It enables communication between NFC-enabled devices when they are brought close together. NFC is enabled in many of the public transport IC cards, credit cards, smartphones, etc., and is widely used in everyday life.
■Types of NFC standards
According to the specifications, the NFC standards fall into three types: Type-A, Type-B, and Type-F. SMK’s NFC antennas support all types of NFC standards.
| Type-A | Type-B | Type-F | |
| Features | NFC standard developed by NXP Semiconductors in the Netherlands | NFC standard developed by Motorola in the USA.Faster processing and better security are achieved with an integrated CPU. | NFC standard developed by Sony in Japan.Extremely high processing speed of approximately 0.1 sec is achieved while maintaining excellent security. |
| Examples of use | - Cigarette purchase card “taspo”, for identification of adults aged 20 and over (in Japan) - Public transport IC cards, such as“Oyster Card” (UK) or “Tmoney” (Korea) | - Identification cards, such as passports, driver's licenses, Basic Resident Register Cards and Individual Number Card (Japan) - Public transport IC cards, such as “Navigo” (France) | - Public transport IC cards, such as “Suica” or “PASMO”, and electronic money, such as “Edy”, “nanaco”, “iD”, or “QUICpay” (Japan) - Public transport IC cards, such as “Octopus” (Hong Kong) |

